14.2.3. Example name spaced nonlinear SDOF¶
The source code is developed by Maxim Millen from University of Porto.
The source code is shown below, which can be downloaded
here.Also download the constants file
here, and theground motion fileMake sure the numpy, matplotlib and eqsig packages are installed in your Python distribution.
Run the source code in your favorite Python program and should see
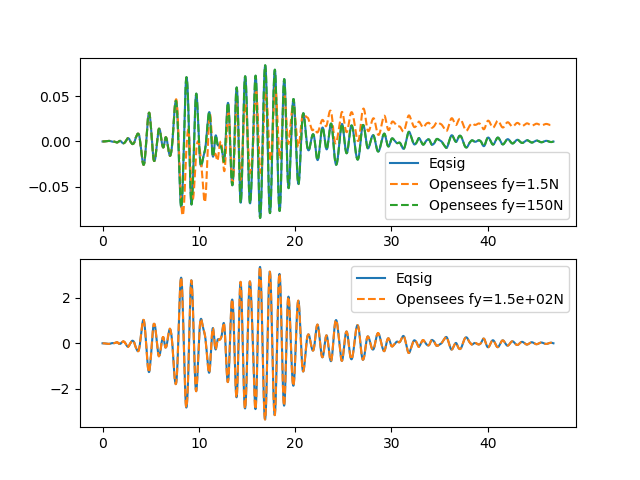
1import eqsig
2from eqsig import duhamels
3import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
4import numpy as np
5
6import openseespy.opensees as op
7import opensees_constants as opc #opensees_constants.py should be close to main file or use sys.path... to its directory
8
9
10def get_inelastic_response(mass, k_spring, f_yield, motion, dt, xi=0.05, r_post=0.0):
11 """
12 Run seismic analysis of a nonlinear SDOF
13
14 :param mass: SDOF mass
15 :param k_spring: spring stiffness
16 :param f_yield: yield strength
17 :param motion: list, acceleration values
18 :param dt: float, time step of acceleration values
19 :param xi: damping ratio
20 :param r_post: post-yield stiffness
21 :return:
22 """
23
24 op.wipe()
25 op.model('basic', '-ndm', 2, '-ndf', 3) # 2 dimensions, 3 dof per node
26
27 # Establish nodes
28 bot_node = 1
29 top_node = 2
30 op.node(bot_node, 0., 0.)
31 op.node(top_node, 0., 0.)
32
33 # Fix bottom node
34 op.fix(top_node, opc.FREE, opc.FIXED, opc.FIXED)
35 op.fix(bot_node, opc.FIXED, opc.FIXED, opc.FIXED)
36 # Set out-of-plane DOFs to be slaved
37 op.equalDOF(1, 2, *[2, 3])
38
39 # nodal mass (weight / g):
40 op.mass(top_node, mass, 0., 0.)
41
42 # Define material
43 bilinear_mat_tag = 1
44 mat_type = "Steel01"
45 mat_props = [f_yield, k_spring, r_post]
46 op.uniaxialMaterial(mat_type, bilinear_mat_tag, *mat_props)
47
48 # Assign zero length element
49 beam_tag = 1
50 op.element('zeroLength', beam_tag, bot_node, top_node, "-mat", bilinear_mat_tag, "-dir", 1, '-doRayleigh', 1)
51
52 # Define the dynamic analysis
53 load_tag_dynamic = 1
54 pattern_tag_dynamic = 1
55
56 values = list(-1 * motion) # should be negative
57 op.timeSeries('Path', load_tag_dynamic, '-dt', dt, '-values', *values)
58 op.pattern('UniformExcitation', pattern_tag_dynamic, opc.X, '-accel', load_tag_dynamic)
59
60 # set damping based on first eigen mode
61 angular_freq = op.eigen('-fullGenLapack', 1) ** 0.5
62 alpha_m = 0.0
63 beta_k = 2 * xi / angular_freq
64 beta_k_comm = 0.0
65 beta_k_init = 0.0
66
67 op.rayleigh(alpha_m, beta_k, beta_k_init, beta_k_comm)
68
69 # Run the dynamic analysis
70
71 op.wipeAnalysis()
72
73 op.algorithm('Newton')
74 op.system('SparseGeneral')
75 op.numberer('RCM')
76 op.constraints('Transformation')
77 op.integrator('Newmark', 0.5, 0.25)
78 op.analysis('Transient')
79
80 tol = 1.0e-10
81 iterations = 10
82 op.test('EnergyIncr', tol, iterations, 0, 2)
83 analysis_time = (len(values) - 1) * dt
84 analysis_dt = 0.001
85 outputs = {
86 "time": [],
87 "rel_disp": [],
88 "rel_accel": [],
89 "rel_vel": [],
90 "force": []
91 }
92
93 while op.getTime() < analysis_time:
94 curr_time = op.getTime()
95 op.analyze(1, analysis_dt)
96 outputs["time"].append(curr_time)
97 outputs["rel_disp"].append(op.nodeDisp(top_node, 1))
98 outputs["rel_vel"].append(op.nodeVel(top_node, 1))
99 outputs["rel_accel"].append(op.nodeAccel(top_node, 1))
100 op.reactions()
101 outputs["force"].append(-op.nodeReaction(bot_node, 1)) # Negative since diff node
102 op.wipe()
103 for item in outputs:
104 outputs[item] = np.array(outputs[item])
105
106 return outputs
107
108
109def show_single_comparison():
110 """
111 Create a plot of an elastic analysis, nonlinear analysis and closed form elastic
112
113 :return:
114 """
115
116 record_filename = 'test_motion_dt0p01.txt'
117 motion_step = 0.01
118 rec = np.loadtxt(record_filename)
119 acc_signal = eqsig.AccSignal(rec, motion_step)
120 period = 1.0
121 xi = 0.05
122 mass = 1.0
123 f_yield = 1.5 # Reduce this to make it nonlinear
124 r_post = 0.0
125
126 periods = np.array([period])
127 resp_u, resp_v, resp_a = duhamels.response_series(motion=rec, dt=motion_step, periods=periods, xi=xi)
128
129 k_spring = 4 * np.pi ** 2 * mass / period ** 2
130 outputs = get_inelastic_response(mass, k_spring, f_yield, rec, motion_step, xi=xi, r_post=r_post)
131 outputs_elastic = get_inelastic_response(mass, k_spring, f_yield * 100, rec, motion_step, xi=xi, r_post=r_post)
132 ux_opensees = outputs["rel_disp"]
133 ux_opensees_elastic = outputs_elastic["rel_disp"]
134
135 bf, sps = plt.subplots(nrows=2)
136 sps[0].plot(acc_signal.time, resp_u[0], label="Eqsig")
137 sps[0].plot(outputs["time"], ux_opensees, label="Opensees fy=%.3gN" % f_yield, ls="--")
138 sps[0].plot(outputs["time"], ux_opensees_elastic, label="Opensees fy=%.3gN" % (f_yield * 100), ls="--")
139 sps[1].plot(acc_signal.time, resp_a[0], label="Eqsig") # Elastic solution
140 time = acc_signal.time
141 acc_opensees_elastic = np.interp(time, outputs_elastic["time"], outputs_elastic["rel_accel"]) - rec
142 print("diff", sum(acc_opensees_elastic - resp_a[0]))
143 sps[1].plot(time, acc_opensees_elastic, label="Opensees fy=%.2gN" % (f_yield * 100), ls="--")
144 sps[0].legend()
145 sps[1].legend()
146 plt.show()
147
148
149if __name__ == '__main__':
150 show_single_comparison()